常考手撕题
死锁
// 死锁的例子
class DeadLockDemo {
private static final Object lock1 = new Object();
private static final Object lock2 = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (lock1) {
System.out.println("线程1获取到了锁1");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (lock2) {
System.out.println("线程1获取到了锁2");
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (lock2) {
System.out.println("线程2获取到了锁2");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (lock1) {
System.out.println("线程2获取到了锁1");
}
}
}).start();
}
}创建线程以及线程池
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(),
threadFactory));threadsPool.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub }
});public class ThreadPoolExecutorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 10, 100, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(10));
// 执行任务
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
final int index = i;
threadPool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(index + " 被执行,线程名:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
}线程
方法1:
//1.创建一个实现了Runnable接口的类
class MThread implements Runnable {
//2.实现类去实现Runnable中的抽象方法:run()
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + i);
}
}
}
}
public class ThreadTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//3.创建实现类的对象
MThread mThread = new MThread();
//4.将此对象作为参数传递到Thread类的构造器中,创建Thread类的对象
Thread t1 = new Thread(mThread);
t1.setName("线程1");
//5.通过Thread类的对象调用start():① 启动线程 ②调用当前线程的run()-->调用了Runnable类型的target的run()
t1.start();
//再启动一个线程,遍历100以内的偶数
Thread t2 = new Thread(mThread);
t2.setName("线程2");
t2.start();
}
}方法二:
//1.创建一个继承于Thread类的子类
class MyThread extends Thread {
//2.重写Thread类的run()
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + i);
}
}
}
}
public class ThreadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//3.创建Thread类的子类的对象
MyThread t1 = new MyThread();
//4.通过此对象调用start():①启动当前线程 ② 调用当前线程的run()
t1.start();
//重新创建一个线程的对象
MyThread t2 = new MyThread();
t2.start();
}
}单例模式
01、饿汉式
public class Singleton {
private static final Singleton instance = new Singleton();
private Singleton() {}
public static Singleton getInstance() {
return instance;
}
}02、懒汉式
public class Singleton {
private static Singleton instance;
private Singleton() {}
public static synchronized Singleton getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new Singleton();
}
return instance;
}
}HashMap
第一,HashMap有3个要素:hash函数+数组+单链表
第二,对于hash函数而言,需要考虑些什么?
要快,对于给定的Key,要能够快速计算出在数组中的index。那么什么运算够快呢?显然是位运算!
要均匀分布,要较少碰撞。我们希望通过hash函数,让数据均匀分布在数组中,不希望大量数据发生碰撞,导致链表过长。那么怎么办到呢?也是利用位运算,通过对数据的二进制的位进行移动,让hash函数得到的数据散列开来,从而减低了碰撞的概率。
如果发生了碰撞怎么办?
拉链法:通过单链表解决。
线性探测法:
如果发生冲突,那么记下这个冲突的位置为index,然后在加上固定步长,即index+step,找到这个位置,看一下是否仍然冲突,如果继续冲突,那么按照这个思路,继续加上固定步长。其实这就是所谓的线性探测来解决Hash冲突的方法!
1、put函数,首先判断需不需要扩容,判断的标准就是,当前的容量*负载因子是不是大于当前已经使用的容量,如果大于了,就要执行resize方法,这个方法会创建一个新的数组,新数组的容量是原来的2倍大小。然后把原来链表里面的元素放到一个容器里面,最后把容器里面的数倒出来,在put到新的数组里面。
如果不需要扩容,那么会利用hash方法,进行一次散列,然后判断当前的Entry数组元素之前有没有被占据,没有直接把这个“坑”占掉,否则,进行链表的遍历,找到了直接修改,没找到,就把元素放在原来头结点的前面(头插法),最后返回旧元素的数值。
2、get方法:依旧是首先利用hash方法对hashcode的值进行二次哈希,然后计算出数组的下标,后面的其实和put差不多,就不细讲了。
哈希函数的设计目标之一就是要尽可能增大小输入值之间的差异,以优化存储和查找效率。对于hashCode()来说,它是Java对象用于哈希集合(如HashMap、HashTable、HashSet等)的默认方法,返回一个整形值。
几点解释这段代码h=key.hashCode())^(h>>16):
h=key.hashCode()这是取键值的哈希,比如通过ASCII转换来实现,每有一个字符的改变,对应的哈希值也就改变了。h>>16这是将哈希值进行右移16位的操作,将前16位移到后16位来,这样的操作能够保证高位和低位的信息都可以参与运算,增加了复杂性,并且使得计算出的哈希值更加均匀地分布。
^(h>>16)这是将原始的哈希值和右移后的哈希值进行异或操作。异或操作的一个重要特点是相同的值异或结果为0,不同的值异或结果为1,通过这样的方式,能够更大程度地增加了哈希值的差异性。
综上,这一哈希值的取法就是为了尽可能让各个键值的哈希结果均匀并且有区分度,从而减少在存储和查找的过程中出现哈希冲突的可能,提升效率。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
// 手撕hashmap
public class MyHashMap<K, V> {
// 内部的属性
private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4;// 默认大小
private static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
private int capacity;
private float load_factor = 0.75f;
private int entryUseSize;// 已经使用的entry的数量
private Entry<K, V>[] table = null;// entry类型的数组
// 构造函数
public MyHashMap() {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY,DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
public MyHashMap(int initial_capacity, float load_factor) {
if (initial_capacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("!!!");
if (load_factor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(load_factor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("!!");
this.capacity = initial_capacity;
this.load_factor = load_factor;
table = new Entry[this.capacity];
}
class Entry<K, V> {
private K key;
private V value;
private Entry<K, V> next;
Entry(K k, V v, Entry<K, V> next) {
this.key = k;
this.value = v;
this.next = next;
}
public K getKey() {
return key;
}
public V getValue() {
return value;
}
}
public V put(K key, V value) {
V oldNum = null;// 需要返回的旧的数
if (this.entryUseSize >= this.capacity * this.load_factor)// 需要扩容
resize(2 * this.capacity);// 扩容以及rehash
int index = hash(key) & (this.capacity - 1);// 利用hash函数再散列一次
// 如果是空直接放进去
if (table[index] == null) {
table[index] = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
++this.entryUseSize;
} else {// 需要遍历链表
Entry<K, V> entry = table[index];
Entry<K, V> e = entry;
while (e != null) {
if (e.getKey() == key || key.equals(e.getKey())) {
oldNum = e.value;
e.value = value;
return oldNum;
}
e = e.next;
}
// 如果没有这个key,使用头插法直接插入
table[index] = new Entry<K, V>(key, value, entry);
++this.entryUseSize;
}
return oldNum;
}
public V get(K key) {
int index = hash(key) & (this.capacity - 1);
if (table[index] == null)
return null;
else {
Entry<K, V> entry = table[index];
do {
if (key == entry.getKey() || key.equals(entry.getKey()))
return entry.getValue();
entry = entry.next;
} while (entry != null);
}
return null;
}
// 根据hashcode来计算散列值
private int hash(K key) {
int h = 0;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >> 16);
}
// 重新划分数组大小,然后把原来的里面的元素都放入新数组,参数newSize表示新的容量
private void resize(int newSize) {
Entry<K, V>[] newTable = new Entry[newSize];
this.capacity = newSize;
this.entryUseSize = 0;
rehash(newTable);
}
// 把原来的数全放到新的输入数组里面
private void rehash(Entry<K, V>[] newTable) {
List<Entry<K, V>> list = new ArrayList<Entry<K, V>>();
for (Entry<K, V> entry : this.table)// 遍历数组里面的每个元素
{
if (entry != null) {
do {// 遍历链表里面的每个元素
list.add(entry);
entry = entry.next;
} while (entry != null);
}
}
if (newTable.length > 0) {
this.table = newTable;// 指向新的数组
}
for (Entry<K, V> entry : list) {
// 调用put函数,把刚才放入list里面的数据放到新的table里
put(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
MyHashMap<String, String> hash = new MyHashMap<String, String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
hash.put("nihao" + i, "buhao" + i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(hash.get("nihao" + i));
}
}
}LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存
LRU 缓存机制可以通过哈希表+双向链表实现,我们用一个哈希表和一个双向链表维护所有在缓存中的键值对。
双向链表按照被使用的顺序存储了这些键值对,靠近头部的键值对是最近使用的,而靠近尾部的键值对是最久未使用的。
哈希表即为普通的哈希映射(HashMap),通过缓存数据的键映射到其在双向链表中的位置。
- 对于 get 操作,首先判断 key 是否存在:
如果 key 不存在,则返回 −1;
如果 key 存在,则 key 对应的节点是最近被使用的节点。通过哈希表定位到该节点在双向链表中的位置,并将其移动到双向链表的头部,最后返回该节点的值。
- 对于 put 操作,首先判断 key 是否存在:
如果 key 不存在,使用 key 和 value 创建一个新的节点,在双向链表的头部添加该节点,并将 key 和该节点添加进哈希表中。然后判断双向链表的节点数是否超出容量,如果超出容量,则删除双向链表的尾部节点,并删除哈希表中对应的项;
如果 key 存在,则与 get 操作类似,先通过哈希表定位,再将对应的节点的值更新为 value,并将该节点移到双向链表的头部。
public class LRUCache {
class DLinkedNode {
int key;
int value;
DLinkedNode prev;
DLinkedNode next;
public DLinkedNode() {}
public DLinkedNode(int _key, int _value) {key = _key; value = _value;}
}
private Map<Integer, DLinkedNode> cache = new HashMap<Integer, DLinkedNode>();
private int size;
private int capacity;
private DLinkedNode head, tail;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.size = 0;
this.capacity = capacity;
// 使用伪头部和伪尾部节点
head = new DLinkedNode();
tail = new DLinkedNode();
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
private void addToHead(DLinkedNode node) {
node.prev = head;
node.next = head.next;
head.next.prev = node;
head.next = node;
}
private void removeNode(DLinkedNode node) {
node.prev.next = node.next;
node.next.prev = node.prev;
}
private void moveToHead(DLinkedNode node) {
removeNode(node);
addToHead(node);
}
private DLinkedNode removeTail() {
DLinkedNode res = tail.prev;
removeNode(res);
return res;
}
public int get(int key) {
DLinkedNode node = cache.get(key);
if (node == null) {
return -1;
}
// 如果 key 存在,先通过哈希表定位,再移到头部
moveToHead(node);
return node.value;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
DLinkedNode node = cache.get(key);
if (node == null) {
// 如果 key 不存在,创建一个新的节点
DLinkedNode newNode = new DLinkedNode(key, value);
// 添加进哈希表
cache.put(key, newNode);
// 添加至双向链表的头部
addToHead(newNode);
++size;
if (size > capacity) {
// 如果超出容量,删除双向链表的尾部节点
DLinkedNode tail = removeTail();
// 删除哈希表中对应的项
cache.remove(tail.key);
--size;
}
}
else {
// 如果 key 存在,先通过哈希表定位,再修改 value,并移到头部
node.value = value;
moveToHead(node);
}
}
}接雨水
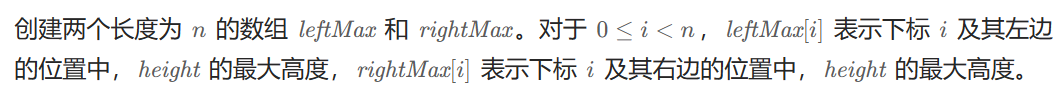

class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
int ans = 0;
int left = 0, right = height.length - 1;
int leftMax = 0, rightMax = 0;
while (left < right) {
leftMax = Math.max(leftMax, height[left]);
rightMax = Math.max(rightMax, height[right]);
if (height[left] < height[right]) {
ans += leftMax - height[left];
++left;
} else {
ans += rightMax - height[right];
--right;
}
}
return ans;
}
}全排列
class Solution {
public static boolean[] st;
public static int n;
public static List<List<Integer>> res;
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
n = nums.length;
st = new boolean[n];
List<Integer> it = new ArrayList<>();
res = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(0, nums, it);
return res;
}
public void dfs(int depth, int[] nums, List<Integer> it){
if (depth == n){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(it));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if (!st[i]){
it.add(nums[i]);
st[i] = true;
dfs(depth + 1, nums, it);
st[i] = false;
it.remove(it.size() - 1);
}
}
}
}多线程打印
两个线程交替打印A1B2C3
import org.junit.Test;
/**
* @author liming
* @date 2020/10/14
* @description 交替打印 A1B2C3 ...
*/
public class AlternatePrint {
static Thread t1 = null, t2 = null;
/**
* 使用 synchronized
*/
@Test
public static void alternatePrint() {
Object lock = new Object();
char[] aI = "1234567".toCharArray();
char[] aC = "ABCDEFG".toCharArray();
t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < aC.length; i++) {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println(aC[i]);
lock.notify();
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
});
t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < aI.length; i++) {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println(aI[i]);
lock.notify();
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
alternatePrint();
}
}两个线程轮流打印1到100
package mianTest;
// 单纯的利用boolean变量来写 加一个volatile关键字:保证他的可见性
public class Demo01 {
volatile static int flag = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread myThread = new Thread(new myThread1());
Thread myThread2 = new Thread(new myThread2());
myThread.start();
myThread2.start();
}
public static class myThread1 implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
int i = 0;
while (i < 10) {
if (flag == 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " = " + i);
i += 2;
flag = 1;
}
}
}
}
public static class myThread2 implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
int i = 1;
while (i < 10) {
if (flag == 1) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " = " + i);
i += 2;
flag = 0;
}
}
}
}
}哲学家进餐问题
该题的本质是考察 如何避免死锁。
而当5个哲学家都左手持有其左边的叉子 或 当5个哲学家都右手持有其右边的叉子时,会发生死锁。
故只需设计1个避免发生上述情况发生的策略即可。
即可以让一部分哲学家优先去获取其左边的叉子,再去获取其右边的叉子;再让剩余哲学家优先去获取其右边的叉子,再去获取其左边的叉子。
class DiningPhilosophers {
//1个Fork视为1个ReentrantLock,5个叉子即5个ReentrantLock,将其都放入数组中
private final ReentrantLock[] lockList = {new ReentrantLock(),
new ReentrantLock(),
new ReentrantLock(),
new ReentrantLock(),
new ReentrantLock()};
public DiningPhilosophers() {
}
// call the run() method of any runnable to execute its code
public void wantsToEat(int philosopher,
Runnable pickLeftFork,
Runnable pickRightFork,
Runnable eat,
Runnable putLeftFork,
Runnable putRightFork) throws InterruptedException {
//philosopher 哲学家的编号。
int leftFork = (philosopher + 1) % 5; //左边的叉子 的编号
int rightFork = philosopher; //右边的叉子 的编号
//编号为偶数的哲学家,优先拿起左边的叉子,再拿起右边的叉子
if (philosopher % 2 == 0) {
lockList[leftFork].lock(); //拿起左边的叉子
lockList[rightFork].lock(); //拿起右边的叉子
}
//编号为奇数的哲学家,优先拿起右边的叉子,再拿起左边的叉子
else {
lockList[rightFork].lock(); //拿起右边的叉子
lockList[leftFork].lock(); //拿起左边的叉子
}
pickLeftFork.run(); //拿起左边的叉子 的具体执行
pickRightFork.run(); //拿起右边的叉子 的具体执行
eat.run(); //吃意大利面 的具体执行
putLeftFork.run(); //放下左边的叉子 的具体执行
putRightFork.run(); //放下右边的叉子 的具体执行
lockList[leftFork].unlock(); //放下左边的叉子
lockList[rightFork].unlock(); //放下右边的叉子
}
}红包随机算法
// 题目2:请编写一个红包随机算法。
// 给定一定的金额,一定的人数,保证每个人都能随机获得一定的金额。
// 比如100元的红包,10个人抢,每人分得一些金额。约束条件为,最佳手气金额不能超过最大金额的90%。
// 请给出java代码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
public class RedPacket {
private int totalAmount;
private int totalPeople;
private Random rnd = new Random();
public RedPacket(int totalAmount, int totalPeople) {
this.totalAmount = totalAmount;
this.totalPeople = totalPeople;
}
public List<Integer> splitRedPacket() {
List<Integer> amounts = new ArrayList<>();
int leftMoney = totalAmount; //红包总额
int leftPeople = totalPeople; //总人数
int bestLuckAmount = (int)(totalAmount * 0.9); //每个人能够获得的最大金额
for (int i = 0; i < totalPeople - 1; i++) {
int amount = rnd.nextInt(Math.min(bestLuckAmount, leftMoney / leftPeople * 2 - 1)) + 1; //随机抽取金额,保证后面的人也至少可以获得1元
amounts.add(amount);
leftMoney -= amount;
leftPeople--;
}
// 最后一个人得到的红包
amounts.add(leftMoney);
return amounts;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
RedPacket redPacket = new RedPacket(100, 10);
List<Integer> amounts = redPacket.splitRedPacket();
for (int i = 0; i < amounts.size(); i++) {
System.out.println("Person " + (i+1) + " gets " + amounts.get(i) + " yuan");
}
}
}